<내용 다운로드>
<슬라이드>
<관련내용>
내가 알던 캐쉬 솔루션
- memcached 기반
- mysql 기반
But, 현실은 이 둘로 만족 못해.
그 이유는 mysql의 persistent, 데이터 크기와 memcache의 1mb데이터 크기 이슈가 있다.
다양한 데이터를 지원하고, replication도 수직/수평으로 되고, 1mb 이상 데이터를 마음대로 쓰고, 속도나 여러 언어에서 사용할 수 있는 그런 캐쉬 솔루션을 원했다.
Redis?
- Vmware (2010.3.15 스폰서)에서 밀고 있음
-Remote Dictionary Server의 약자
-Key-value store, Cache
-사용하는 곳: Github, blizzard, digg, stackoverflow
-최신 버전 : 2.2.12 (stable) 2011/08/17
-
http://redis.io/
장점
- Persistence
- Speed (간단한 데이터 2백만 건을 1.28초에 저장)
- Data Structure
- Atomic Operation (tx)
- Sharding / Replication 의 용이
- Pub/sub / notification (message queue 또는 comet) - real time
- String(1G), Hash, List, Set, Sorted Set(score필요), intersection, union, difference
- In-memory
- 데이터 TTL, Expire
- Node.js를 포함하는 클라이언트가 다양한 언어에서 구현.
- operation cost : O(1)
- Multiple Instance에 접속해서 item를 수집(select)후 옮길(move) 수 있음(locking지원)
단점 / 이슈
- Ram mode에서는 이슈는 없지만, VM mode 를 이용해서 메모리 관리할 때 속도가 많이 느려짐
- In-memory라 메모리보다 큰 데이터는 적합하지 않을 수 있음(VM 모드를 사용할 때는 메모리 제한이 없음) -> 2.4부터 VM 모드 deprecated
Persistence 의 snapshotting 이용시 I/O 이슈가 있음
- 소스 컴파일 설치
- Sharding을 클라이언트에서 잘 지정할 필요가 있음
- Replication시 blocking됨 (2.4부터 non-blocking하면서 속도개선)
왜 Redis를 주목하는가?
- Vmware의 CloudFoundry Stroage 엔진으로 사용 (mysql, mongoDB와 함께 선정).
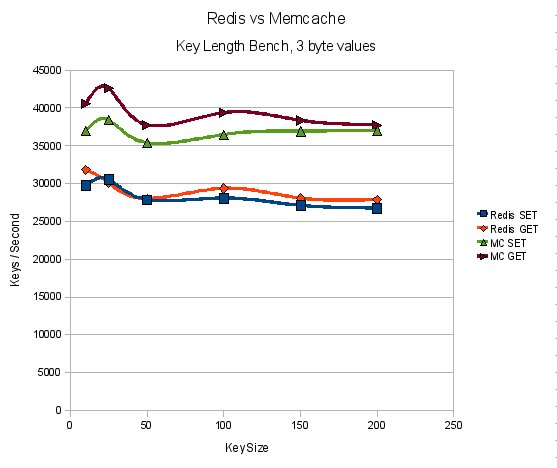
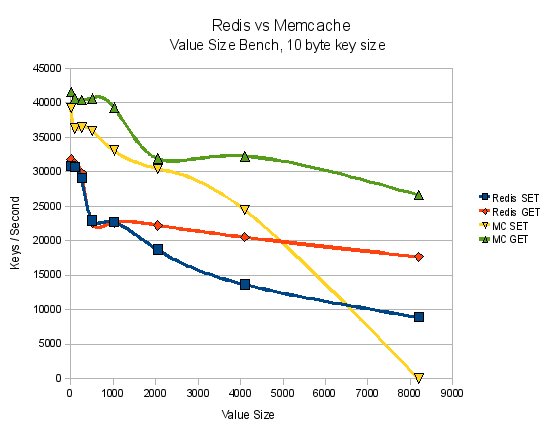
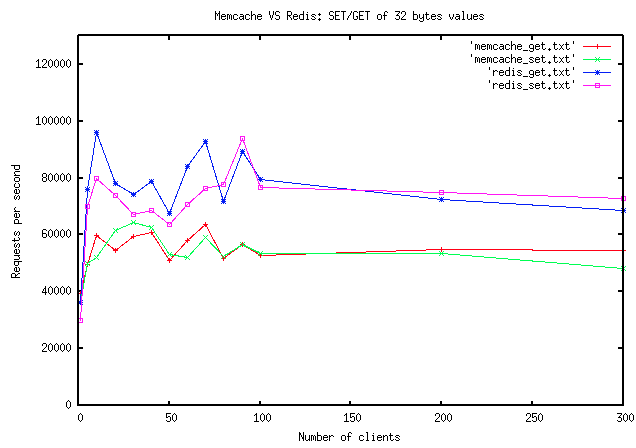
- 성능은 memcached와 비슷 함 (리얼 환경에 따라 달라질 수 있음)
- Non blocking IO, Single Threaded
- epoll, kqueue and select 이용
- Libevent (이벤트 처리 오픈 소스) 를 이용하는 대신 자체 구현.
=> Dependent가 없음. 심플해지는 코드
- Single-thread Server
- ANSI C 구현
- 임베디드 / 서버에서 porting이 편함
- Portable 코드!
- 2.4부터는 비동기로 Replication 구성이 가능
* Node.js + redis 사용하는 사례들이 최근에 늘고 있음
* 2011년 안으로 Redis clustering을 구현할 예정 (처음부터 분산 테이블을 목표로 만들어졌기 때문에 이 부분이 구현되면 엄청난 일이 벌어질 듯..)
2.4 Release 내용들
http://antirez.com/post/everything-about-redis-24
Redis Main 개발자 블로그
- 속도개선
- Replication시 non-blocking으로 동작
- jemalloc 추가
- set또는 list에 multi adding 기능
- 그외짜잘한 성능/기선 개선
간단한 데모
http://try.redis-db.com
2.0.2 version 이라서 그 이상의 버전에서 제공하는 API를 활용할 수 없음
- mset 버그 있음..
설치/실행 방법
// 설치 (http://redis.io/download)
$ wget http://redis.googlecode.com/files/redis-2.2.12.tar.gz
$ tar xzf redis-2.2.12.tar.gz
$ cd redis-2.2.12
$ make
// 데몬 실행
$ cd src
$ cd redis-server
(daemon).. Log..
// 클라이언트 실행 - 다른 쉘에서 실행
$ cd 소스설치/src ; redis-cli
redis> set foo bar
OK
redis> get foo
"bar"
예제 코드
> set hello world
"OK"
> get hello
"world"
> set a 1
‘1’
> expire a 100
true
> get a
"`1"
> get a
"`1“
(100초 뒤)
> get a
null
> set foo 0
"OK"
> incr foo
1
> incr foo
2
> incr foo
3
> get foo
"3“
> decr foo
2
> set hello world
"OK"
> get hello
"world"
> exists hello
true
> type hello
"string"
> rename hello olleh
"OK"
> get olleh
"world"
> del olleh
1
> get olleh
null
> set a 1
"OK"
> set b 2
"OK"
> set c 3
"OK"
> mget a b c
["1","2","3"]
> sadd seta foo
true
> sadd seta bar
true
> sadd setb foo
true
> sinter seta setb
["foo"]
> lpush list a
1
> lpush list b
2
> lpush list c
3
> lpush list d
4
> lrange list 0 2
["d","c","b"]
> lrange list 0 3
["d","c","b","a"]
> lrange list 2 3
["b","a"]
> sadd set 1
true
> sadd set 2
true
> sadd set 3
true
> smembers set
["3","1","2"]
> zadd ss 1 aa
true
> zadd ss 10 zz
true
> zadd ss 9 yy
true
> zadd ss 2 bb
true
> zrange ss 0 -1
["aa","bb","yy","zz"]
> hset user:1 name x
true
> hset user:1 lastname y
true
> hset user:2 name aa
true
> hget user:1
wrong number of arguments (1 for 2)
> hget user:1 name
"x"
> hgetall user:1
{"name":"x","lastname":"y"}
> hget user:2
wrong number of arguments (1 for 2)
> hget user:2 name
"aa"
> multi
"OK"
> lpush clist a
"QUEUED"
> lpush clist b
"QUEUED"
> lpush clist c
"QUEUED"
> lrange clist 0 -1
"QUEUED"
> exec
[1,2,3,["c","b","a"]]
> multi
"OK"
> lpush dlist a
"QUEUED"
> lpush dlist b
"QUEUED"
> discard
"OK"
pub/sub 코드
1. subscribe 함
[test /home/www/redis/redis-2.2.12/src]# ./redis-cli
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> psubscribe news.article.*;
Reading messages... (press Ctrl-C to quit)
1) "psubscribe"
2) "news.*;"
3) (integer) 1
2. publish 함
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> set article.tech.1000 "Google"
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> sadd article.tech 1000
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> publish news.article.tech 1000
QUEUED
redis 127.0.0.1:6379> exec
1) OK
2) (integer) 1
3) (integer) 0
3. subscribe 하던 부분에서 subscription 받음
1) "pmessage"
2) "news.article.*"
3) "news.article.tech"
4) "1000"
java client API - jedis (가장 괜찮은 것 같음)
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
<type>jar</type>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
가장 좋은 java 클라이언트 라이브러리
- https://github.com/xetorthio/jedis
- 자바의 Map, Set 같은 Collection과 연동되어 사용 가능
- Sharding이 지원되다고 적혀있지만, 테스트는 해보지 않음
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/restful")
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.ACCEPTED)
public class RestfulController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/set/key/{key}/value/{value}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getString(@PathVariable String key, @PathVariable String value, ModelMap model) {
System.out.println("key : " + key);
System.out.println("value : " + value);
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("1.1.1.1");
jedis.set(key, value);
String kValue = jedis.get(key);
model.addAttribute("key", key);
model.addAttribute("value", kValue);
return "test";
}
}
운영상 장점
- 백업은 리얼타임으로 진행
-0 Master – Slave Replication이 수직/수평적으로 scale 가능
- (지금 당장은 없지만) 올해 안으로 Clustering 기능 추가 예정
https://github.com/antirez/redis/blob/master/design-documents/REDIS-CLUSTER
- 대형 데이터 cache용 용도로 생각
memcached는 크기가 큰 데이터에 취약
- Slave 구성시 서버를 내리지 않고 사용가능. Replication 순서
slave asks for SYNC
master BGSAVE, slave waits
master BGSAVE finished, the initial bulk data (the .rdb file) is transfered to slave
master accumulates all the new differences for the slave
master finishes sending the whole initial rdb file to slave
master start feeding the slave with the accumulated buffer, and with anything new arriving from clients, if they are writes.
운영상 이슈 & 편리
- 메모리에 있는 데이터들을 File system으로 덤프
1) Snapshotting (디폴트)
자식 프로세스 실행(fork)하고 자식프로세스가 임시(new) RDB파일 만들고, 그것을 다 저장하면 예전(old) 파일 이름으로 교체 (copy-on-write)
속도 이슈로 인해서 많이 고민했음
2) Append-only file (AOF) - 괜찮은 방법
2.0과 2.2가 절차가 다름.
만약 Snapshotting 하다가 Kill 되거나 비정상적 종료에 대비해서 실행 로그들을 따로 저장(Log Rewriting)하여 만약 재시작시 상태를 유지하기 위해서 AOF 파일을 읽음
자식 프로세스 실행(fork)하고, 자식 프로세스는 임시 AOF 파일을 저장한다. 부모 프로세스는 in-memory buffer에 새로 변경된 내용을 계산한다. 자식 프로세스는 쓰기 작업이 완료후에 부모 프로세스는 in-memory buffer의 내용을 AOF 파일에 저장한다. 새로운 파일로 교체.
운영상 편리
AOF를 이용한다면, 서버 관점에서는 정지시간 없이 Redis 재시작 / 업그레이드 가능 (서버 편함)
환경
설정 정보 변경시 재실행
새로운 버전의 redis 서버 재실행
포트 변경 필요,
서버의 포트를 변경하기 때문에 client의 서버 접속 포트를 수정하고 재시작 필요. (client 불편)
=> 오히려 이거 불편. 기존 방법 사용 필요
운영에 대한 모니터링툴 지원
https://scoutapp.com/plugin_urls/271-redis-monitoring
운영상, cache hit에 대한 정확한 내용은 필요없음. 요청오면 요청 그대로 보내주는 걸로..

운영상 불편할 점
- consistent hashing 을 지원하는 client를 이용해야 distribute 가능
- Sharding을 일일이 클라이언트 API를 이용해서 해줘야 함. API에서 반드시 지원
용도
- Ehcache 와 같이 expire 해도 되는 item 용도
- counter
- 최근 30개를 순서대로
- 랭킹 정보
- 일반 캐쉬 용도
Arcus 개발팀 Redis 한계를 지적한 부분 (SDEC 2011.6)
Radis 1.2 검토 대비 최신 버전 2.2 비교
- Sorted set에는 no (offset, count) option
=> 최신 버전에서는 offset, count 기능 추가
- No capped collection
=> 용량제한이 있으며, FIFO기능을 갖고 있는 고성능의 테이블을 capped collection이라고 함. 원래 Redis 지원 안함. 원래 빠르게 개발하면 의미가 없어짐
- Not enough cache statistics
- Cannot control memory use
=> info 명령어를 이용해서 간단하게 메모리 사용량 측정 가능
공부했던 레퍼런스 자료들
http://redis.io/ , http://redis.io/topics/faq
http://simonwillison.net/static/2010/redis-tutorial/
http://www.slideshare.net/tag/redis/
http://blog.mjrusso.com/2010/10/17/redis-from-the-ground-up.html
http://www.slideshare.net/Cyworld/004-cto
http://pauladamsmith.com/articles/redis-under-the-hood.html
http://hi.baidu.com/roger_long/blog/item/611b1d017f57f89de950cd87.html
http://redis.io/presentation/Redis_Cluster.pdf
http://www.slideshare.net/karmi/redis-the-ak47-of-postrelational-databases
http://pauladamsmith.com/blog/2011/03/redis_get_set.html




 Redis맛보기.pdf
Redis맛보기.pdf